 ASME code design rules use an allowable stress design philosophy. In this type of engineering design, the true expected loads are defined, and a stress in each component is calculated from those loads. That calculated stress is then compared to a certain “allowable stress” for that material. If the design stress exceeds the allowable stress, then the component design must be changed. The allowable stress is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without failure.
ASME code design rules use an allowable stress design philosophy. In this type of engineering design, the true expected loads are defined, and a stress in each component is calculated from those loads. That calculated stress is then compared to a certain “allowable stress” for that material. If the design stress exceeds the allowable stress, then the component design must be changed. The allowable stress is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without failure.
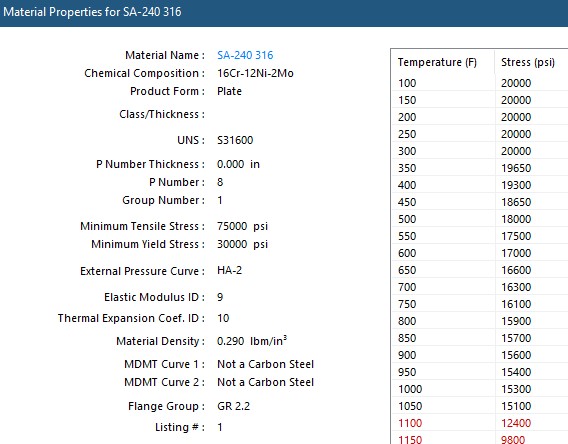
The code publishes allowable stresses for all code materials at various temperatures in Section II, Part D. The allowable stress values are determined for each material by using the lesser of tensile strength divided by 3.5, or 2/3 of yield strength (creep is also considered at elevated temperatures). This ensures that all ASME equipment has a built-in safety factor of overdesign and will be able to maintain structural integrity and safety throughout its service life.